Biofuel is an integral part of the global strategy to become carbon neutral by 2050.
Biofuel tends to have a smaller carbon footprint compared to gasoline and can be easily incorporated into existing transportation and heating infrastructure in the UK.
At AquaSwitch, we think it is essential for any business that has its own vehicles and uses gas heating appliances to understand the basics of biofuels and how this could affect your business’s carbon footprint.
What is biofuel, and is it renewable?
Biofuels are any fuel that is derived from biomass. Put simply, this is fuel in liquid or gas form, which is extracted from plants, algae and even animal waste. And since this source of biomass is readily replenished, biofuels are considered renewable energy.
It should be noted that biomass and biofuels are often used interchangeably as biomass can be directly used as fuel (e.g. burning wood pellets).
However, by definition, biofuels must be in gaseous or liquid form and normally require an additional layer of processing from the original organic material.
What is biofuel used for?
Biofuels are predominantly used in the transportation industry as a replacement or in combination with gasoline. The IEA (International Energy Agency) aims to see a quarter of the world’s transportation run by biofuels by 2050.
However, there has been an increase in the use of biofuels for heating applications, especially since the recent hike in gas prices.
How is biofuel made?
Biofuels can be divided into two broad categories: Biodiesels and Bioethanols.
Biodiesels are oily liquids produced from fats or oils such as tallow (animal fat) and vegetable oils. Their prime advantage is that they are compatible with existing diesel engines and infrastructure and may be blended with gasoline to use in normal engines.
Bioethanols are alcohols produced from the fermentation of sugar or starch, generally from crops such as corn, sugarcane or sugar beet, or other sources such as animal waste.
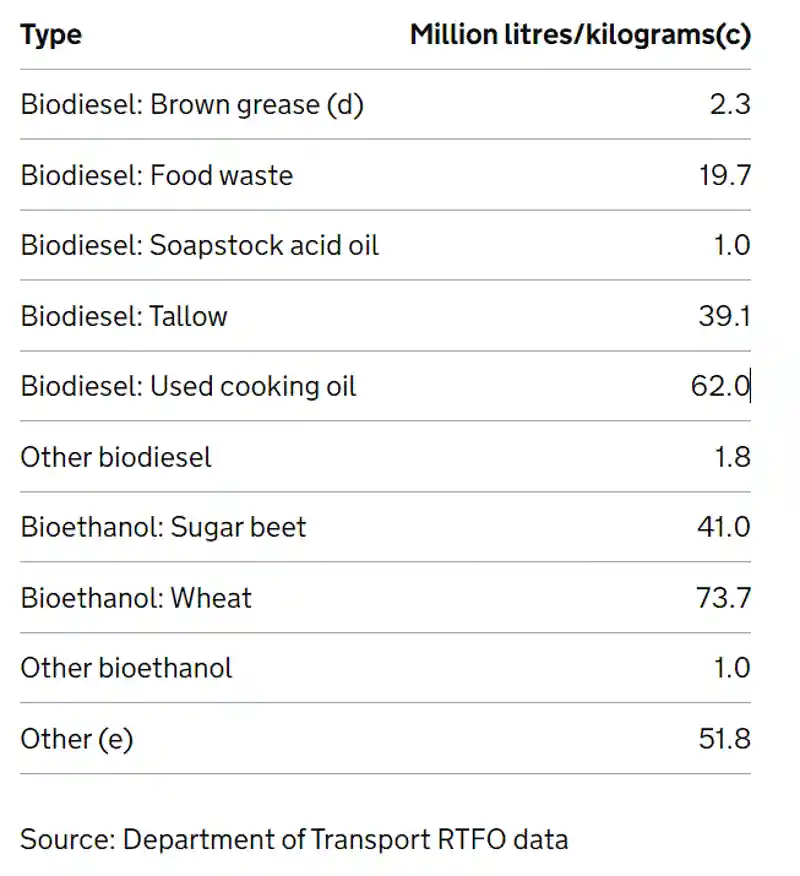
The table below (adapted from DEFRA) shows the number of biofuels produced in the UK by their origin material.
Are biofuels carbon neutral?
Unfortunately, since biofuels are carbon-based organic matter, they release greenhouse gasses when combusted, which means that they do have a carbon footprint.
However, this depends on its source material and the process in which it was produced, with some experimental algal-sources biofuels being deemed very close to carbon neutral.
How can biofuels help reduce global warming?
It is generally accepted that most biofuels have a lower carbon footprint than fossil fuels and are therefore beneficial in the fight against climate change by reducing a business’s carbon footprint.
Making transportation greener
Transport vehicles such as cars, lorries, aeroplanes and diesel trains require a portable energy source to run. Since battery technology is not yet fully developed, biofuels are currently one of the best green energy alternatives.
Making gas heating greener
Furthermore, since heating in the UK is predominantly gas-based, biofuels are set to become an integral part of gas utilities, either in combination or as a replacement for natural gas.
At AquaSwitch, we speculate that it is only a matter of time for green incentives such as the climate change levy to reach this sector, with gas suppliers who source biofuels getting both financial and carbon accounting benefits.
Can cars run on biofuel?
The answer to this question is not so simple. The answer is no unless a vehicle is not specifically designed to run purely on biofuels. However, most cars, utility vans and lorries can run on blended fuel mixtures composed of 10% biofuels.
E10 and E5 fuel found in many UK petrol stations contain 10% and 5% bioethanol mixed in with the gasoline.

