Students who are blind are provided with braille books. An autistic student uses a visual schedule. A student with a learning disability receives additional reading instruction. These students all receive special education services.
Special education provides services that meet the unique needs of each student. This means that special education can include:
- An individualized curriculum that is different than general education peers’
- A curriculum that is modified for a student
- A combination of both
Here’s a roundup of everything you need to know about special education, plus our best special education articles.
What laws are involved in special education?
The Individuals With Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is the federal law that explains how states must address special education. The IDEA definition of special education is: specially designed instruction, at no cost to parents, to meet the unique needs of a child with a disability. It includes physical education, related services (e.g., speech therapy, occupational therapy), vocational education, and travel training. Essentially, special education is how students with disabilities have their needs met in the public education system.
Image: PRC
Read more: What Is IDEA?
What about state laws?
IDEA sets the standard at the federal level, but the process and system are set up at the state level. So what special education looks like varies from state to state.
Visit your state’s Department of Special Education website or check out the parent resource center (every state has one) for information related to special education aimed at parents.
Find your state’s parent resource center in this list from Center for Parent Information & Resources.
How is special education not a “place”?
Special education can occur in many different settings, from the general education classroom to a hospital or separate school. Where a child receives services depends on their needs as determined by the IEP team, which includes the parents.
What are the main components of special education? (What do the acronyms stand for?)
FAPE
Image: Pathfinder Services of ND
FAPE is Free Appropriate Public Education. This essentially means that students with disabilities must be provided with their education at no cost to the parents, just like any other student.
Read more: What Is FAPE?
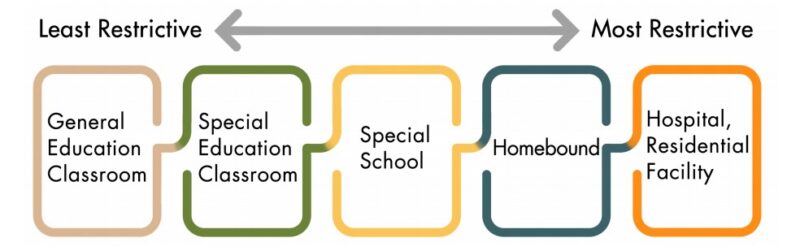
LRE
Image: Arizona Department of Education
LRE is Least Restrictive Environment. LRE is the setting where the child receives services and can vary from general education to a separate school or even the child’s home. The LRE is decided by the IEP team. According to IDEA, special education must be provided in the least restrictive environment, or the same environment as their nondisabled peers, “to the greatest extent possible.” This means that children should only be removed from general education when their disability is such that that they cannot make progress. So, all consideration of where a child will learn starts in general education and works back from there.
Read more: What Is Least Restrictive Environment?
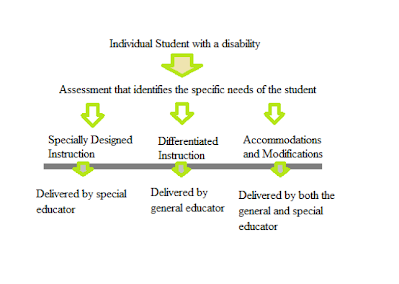
SDI
Image: Coastal Carolina University
SDI is specially designed instruction. This is the foundation of what special education is based on—that every child receives the instruction that they need to make progress and advance toward goals. SDI means adapting the content, delivery, or methodology of instruction to address the child’s needs, as determined by the needs related to their disability. The focus is on helping the child meet educational standards and ensuring access to the general curriculum. To help children access general education curriculum, SDI provides adaptations, accommodations, and modifications.
Read more: What Is Specially Designed Instruction?
IEP
IEP is the Individual Education Program. The IEP is the document that outlines everything that a child requires to receive FAPE and SDI.
Read more: What Is an IEP?
Accommodations and Modifications
Image: The Bender Bunch
Accommodations and modifications are ways that SDI is delivered and how the curriculum is individualized for a child; ways that the child receives access to the general education curriculum. In short, accommodations change how the material is being presented in a way that helps the child overcome or access through the disability. Modifications change what a child is taught or how the child works at school. So, an accommodation would be: allowing a child to record rather than write their answers, or reading aloud a question rather than having them read it. A modification would be providing a child a text with visuals instead of the general education text, or providing a test with two answer choices instead of four.
Read more: Accommodations vs. Modifications: What’s the difference?
Bookmark: 80+ Accommodations Every Special Ed Teacher Should Bookmark
More IDEA terms are defined at Parent Center Hub.
Which students can receive special education and who decides?
Special education is provided to students who fall under one of 13 disability categories:
- Developmental delay
- Specific learning disability
- Speech impairment
- Other health impairment
- Traumatic brain injury
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Vision impairment
- Hearing impairment
- Deaf-blindness
- Emotional disability
- Orthopedic impairment
- Intellectual disability
- Multiple disabilities
In order to receive special education services, a student must be found eligible. This means that they have one of the 13 disabilities and that it impacts them in the school setting. If the child cannot make progress in the general curriculum without SDI, they are eligible for special education services. (If they can make progress but still have an outside diagnosis, they may have a 504 plan in place instead.)
Read more: What Is a 504 plan?
An evaluation is different for each disability category (for example, an evaluation for traumatic brain injury will include a medical evaluation, while an evaluation for speech impairment will not). These regulations vary from state to state so it’s important to know your state’s requirements and timeline.
What is in an IEP?
The IEP includes all the information that the team needs to educate a child with a disability. It only addresses the aspects of a child’s disability that impact them throughout the school day. The sections of an IEP are:
- Present levels: How the child is currently doing in school and how the disability impacts them in class.
- Annual goals: Goals that the child will work on through SDI.
- Objectives: Students who take alternate assessments will also have objectives towards their goals.
- Measuring and reporting progress: Ways that the child’s progress is going to be measured and how it will be reported to parents.
- Specially designed instruction: A statement about how special education and related services will be provided.
- Related services include any therapies (speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy).
- Supplementary aids and services provide access to participation across academic, extracurricular, and nonacademic settings.
- Program modifications for school personnel, which include things that school personnel need to know in order to work with this student (for example, how to use an assisted communication device).
- Extent of nonparticipation is the explanation of how much, if any, the child will be outside of general education, and why the team made that decision.
- Accommodations that the student will be provided during classroom instruction.
- Accommodations that a student will receive during district and state testing.
- Service delivery includes when, where, and how long a child will receive SDI (for example, 30 minutes 1x/week in special education).
- Transition planning for life after secondary school starts no later than a child’s 16th birthday (and can start earlier).
- Age of majority: An IEP must include a statement about how the student understands their rights as they graduate from the IEP.
What happens in an IEP meeting?
There are many different reasons to come together around an IEP, but every year, each student who has an IEP will have an annual review. During an annual review meeting, the team (parent, teachers, a district representative, therapists) discuss the child, their progress, and next steps. Everything in the IEP should be based on data, so it’s important to bring information (e.g., work samples, test data) to review.
Any decision regarding an IEP is a team decision, and team members don’t always agree. If the meeting cannot resolve a concern, schools or parents can follow procedures to reach an agreement.
Read more: What Is an IEP meeting?
Read more: What Is a Manifestation Determination Meeting?
When does special education start and end?
A child can receive early intervention or special education services if they have a disability diagnosed before age 3 (such as Down syndrome) or if they are at risk of a delay.
Read more: What Is Early Intervention?
The end-date for a student who has an IEP depends on a few things. They may be reevaluated and found no longer eligible, in which case special education services would end at that point. Otherwise they are no long eligible when they graduate from high school or turn 22.
What is NOT special education?
There are misconceptions about special education. Some things that special education is not:
- Tutoring
- A specific program, like Orton-Gillingham
- Differentiated instruction
- An inclusive classroom
What else should I know?
Here are more of our favorite special education resources:
What Is Inclusion in Education?
27+ Best Autism Resources for Educators
If you’re still using these five words for students with disabilities, it’s time to stop.
New Ways To Empower Students Who Have Learning Differences or Dyslexia
How Teachers Can Support Twice-Exceptional Students
Resources
The IEP From A to Z: How To Create Meaningful and Measurable Goals and Objectives by Diane Twachtman-Cullen and Jennifer Twachtman-Bassett
10 Critical Components for Success in the Special Education Classroom by Marcia Rohrer and Nannette Samson
Wrightslaw: All About IEPs by Peter Wright, Pamela Wright, and Sandra Webb O’Connor
Do you teach special education? Connect with other teachers on the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
For more articles like this one, subscribe to our newsletters.