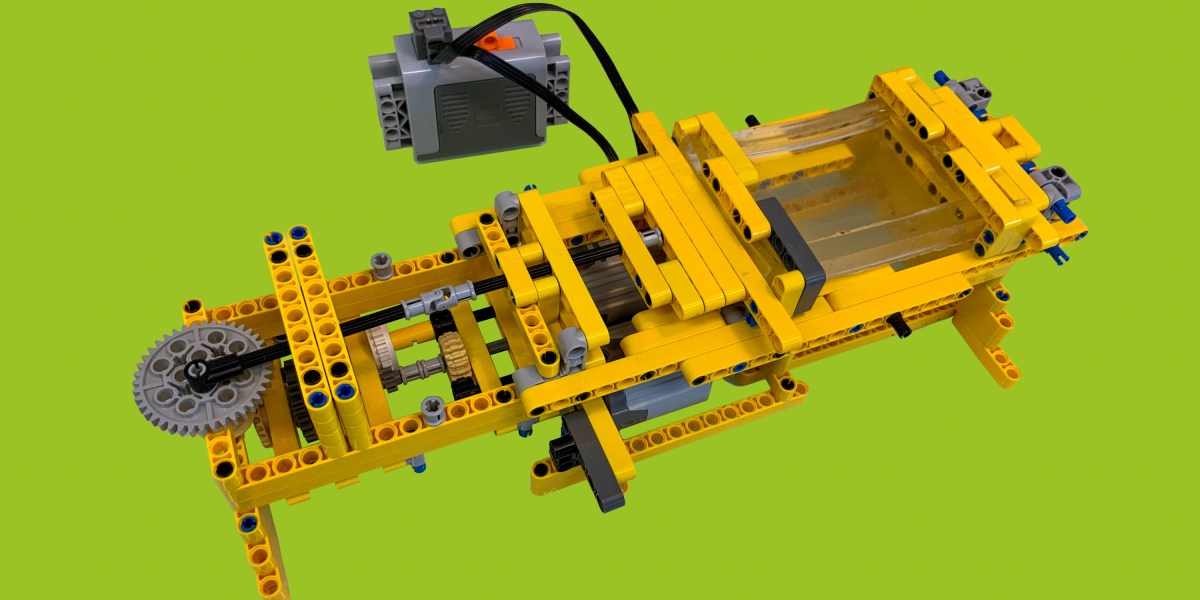
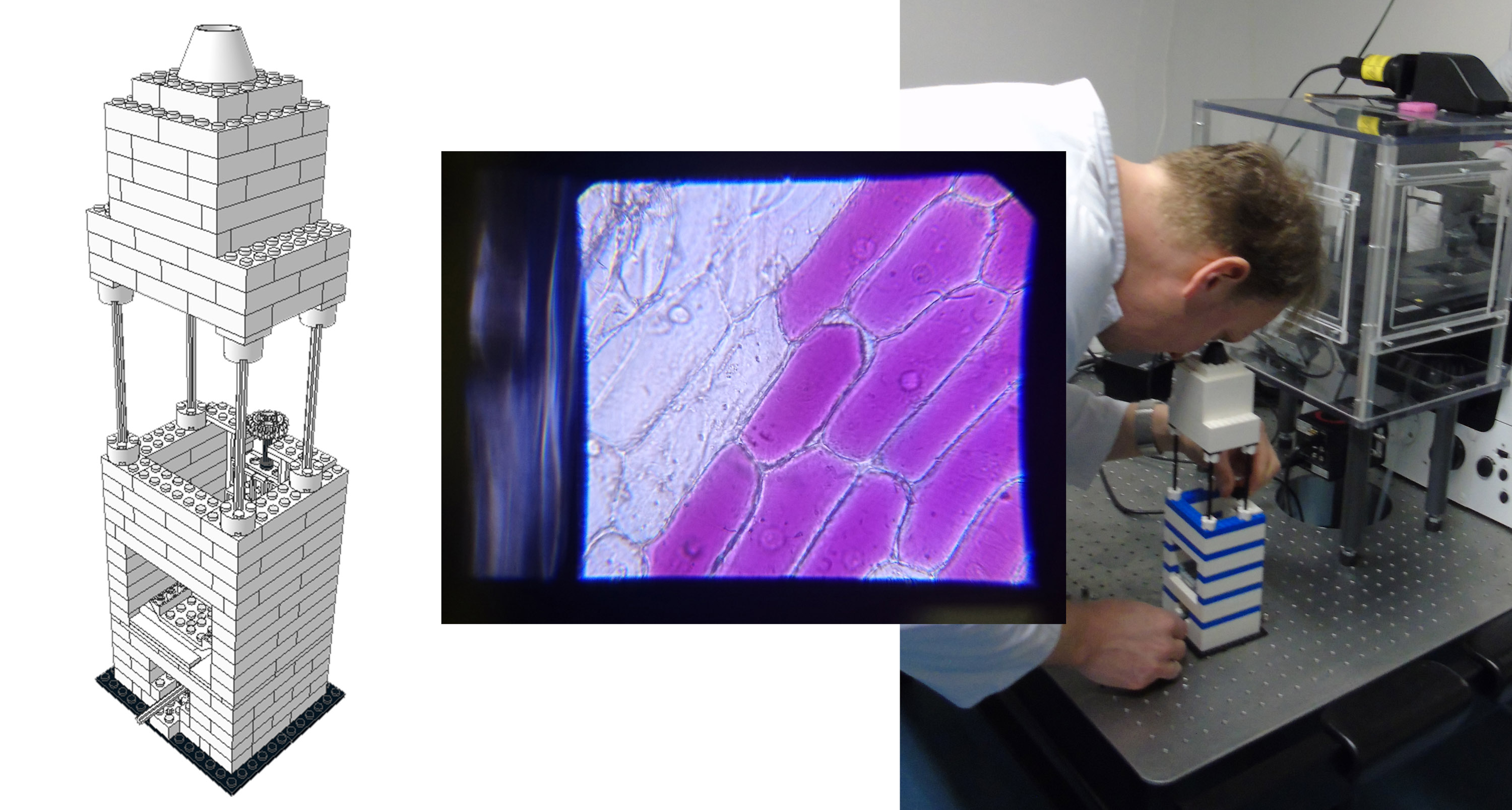
At Cardiff University in Wales, Christopher Thomas, Oliver Castell, and Sion Coulman had similar success building an instrument capable of printing cells. The researchers study skin diseases, lipids (fatty compounds) in the body, and wound healing. Ethically obtained samples are hard to find, so they created a 3D bioprinter out of Lego pieces that is capable of “printing” a human skin analogue, laying down layers of bio-ink that contains living cells. These printers normally cost over a quarter of a million dollars, but they built their version for a mere $550. At first, their colleagues were skeptical that components typically treated as toys could be used in such a professional setting, but after seeing the printer at work, they were quickly convinced. The team made national news, and other groups replicated the model in their own labs.
COURTESY OF CARDIFF UNIVERSITY
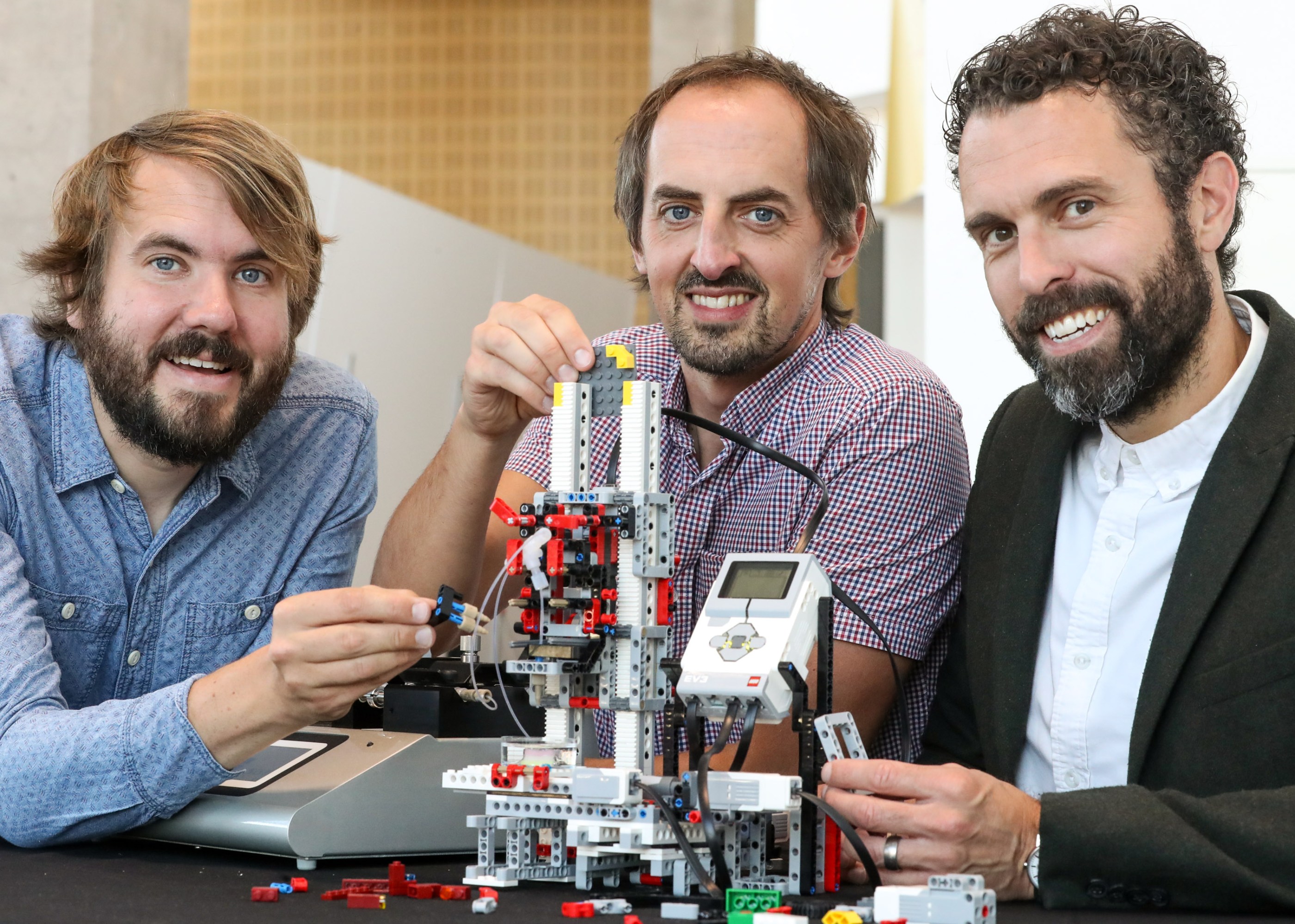
Some scientists are devising tools to take into the classroom. Timo Betz of the University of Göttingen in Germany came up with the idea of building a Lego microscope one day while watching his son, Emil, then eight, play. Betz was scheduled to speak about science at a local school that afternoon but was reluctant to take his own lab-grade microscope into the classroom. His son was immediately on board. “Let’s do this!” he told his dad. Together with Bart Vos, a colleague at the university, they built a microscope that consisted entirely of Lego pieces, with the exception of two optical lenses. Their plans, which they’ve made available to the public, can be used by students as young as 12 to learn the basic concepts of optics.
COURTESY OF TIMO BETZ
Many of these scientists make their models open source, providing them to interested groups or publishing the plans on GitHub or in papers or so that other labs can make their own versions. This is great for researchers the world over, especially those with limited funding—whether they’re new faculty members, scientists at smaller universities, or people working in low-income countries. It’s how a small plastic brick is making science more accessible to all.
Elizabeth Fernandez is a freelance science writer.