“What kind of frogs can you find in the United States?”
I love finding, observing, and hearing frogs!
Even as a kid, I used to patrol the swamps by my house, catching them and then trying to sell them as pets to cars passing by. As you can imagine, no one was interested in buying my frogs, and I ended up letting them go at the end of each day. 🙂
Today, I’m providing a guide to teach you about the different kinds of frogs found in the United States.
One of the BEST ways to find frogs is to learn the noises they make. So, in addition to pictures, you will find audio samples for each species below!
40 Frog Species in the United States:
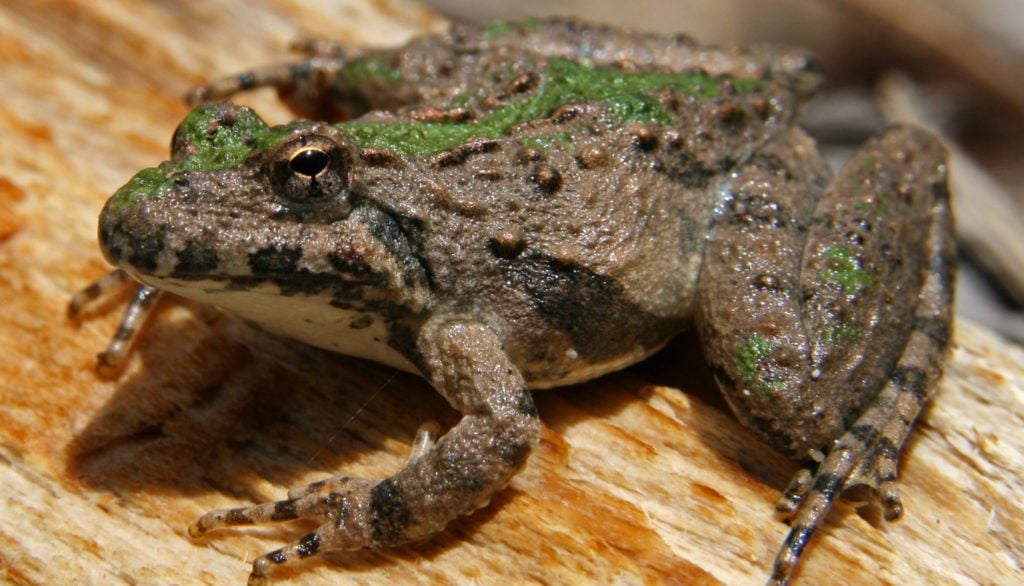
#1. American Bullfrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 3.6 to 6 inches.
- Coloration is typically olive green, with some individuals having gray or brown mottling or spots.
- Fully webbed back feet.
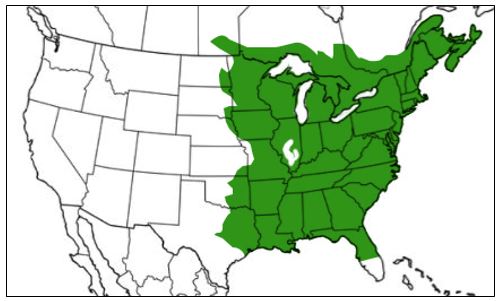
The American Bullfrog is the largest frog in the United States!
Believe it or not, they can grow to weigh as much as 1.5 pounds (.7 kg).
American Bullfrog Range Map
Green = native range. Red = introduced range.
Bullfrogs can be found in permanent bodies of water, including swamps, ponds, and lakes. During the breeding season, the male frogs select egg sites in shallow waters, which they defend aggressively. A female will then select a male by entering his territory.
They are named for their deep call, which is thought to sound like a bull bellowing.
Bullfrogs are known to eat just about anything they can fit in their mouth and swallow! The list of prey includes other frogs, fish, turtles, small birds, bats, rodents, insects, crustaceans, and worms. I have personally witnessed one even trying to eat a baby duck!
#2. Northern Leopard Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 2 to 4.5 inches long.
- Smooth skin is green, brown, or yellow-green with large dark spots.
- Lighter-colored raised ridges extend down the length of the back.
You can spot Northern Leopard Frogs in the United States near slow-moving bodies of water with lots of vegetation. You might see them in or near ponds, lakes, streams, and marshes. I love how bright green most individuals appear!
Northern Leopard Frog Range Map
Due to their fairly large size, these frogs eat various foods, including worms, crickets, flies, and small frogs, snakes, and birds. In one study, a bat was even observed being eaten!
During the spring breeding season, the males will float in shallow pools emitting a low call thought to sound a bit like snoring. The Northern Leopard Frog may also make a high, loud, screaming call if captured or startled.
Northern Leopard Frog populations are declining in many areas, and the cause is not exactly known. It’s thought to be some combination of habitat loss, drought, introduced fish, environmental contaminants, and disease.
#3. Green Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 2 to 4 inches, and the females are typically larger than males.
- Coloration is normally green or brown with darker mottling or spots on the back.
- Ridges run down the sides of the back and they have webbed hind feet.
Green Frogs are one of the easiest frogs to find in the United States.
Green Frog Range Map
Look for them in permanent bodies of water, including lakes, ponds, swamps, and streams. They spend most of their time near the shoreline but jump into deeper water when approached. They also breed and lay eggs near the shore, typically in areas with aquatic vegetation.
The Green Frog produces a single note call that is relatively easy to identify. Listen for a noise that sounds like a plucked banjo string, which is often repeated.
To hunt, they use a “sit and wait” approach, so they are fairly opportunistic. Green Frogs will try to eat almost anything they can fit inside their mouth. The list includes spiders, insects, fish, crayfish, snails, slugs, small snakes, and even other frogs!
#4. Spring Peeper
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are small and range from 1 to 1.5 inches long.
- They’re typically tan or brown, with the females being lighter in color.
- Both males and females usually feature a darker cross or ‘X’ on their back.
These tiny frogs can be found all over the eastern United States.
You’ll typically spot Spring Peepers on the forest floor among the leaves. However, they do have large toe pads that they use for climbing trees.
Spring Peeper Range Map
You can find them in ponds and small bodies of water in the spring, where they breed and lay eggs. After hatching, the young frogs remain in the tadpole stage for about three months before leaving the water.
Spring Peepers get their name from their distinctive spring chorus. They’re thought to sound a bit like baby chickens’ peeps, and they are most often heard in early spring! LISTEN BELOW!
Their calls are very distinctive, and once you know what to listen for, these frogs are very easy to identify by sound.
#5. Gray Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 1.5 to 2 inches.
- Mottled gray, green, and brown coloring. Look for a whitish spot beneath each eye.
- Bumpy skin, short snouts, and bright orange on the undersides of their legs.
Chameleons aren’t the only animal that can change colors! This incredible frog can slowly change colors to match what it’s sitting on to camouflage itself. They can vary from gray to green or brown. It’s common for their back to display a mottled coloring, much like lichen.
Gray Treefrogs are ubiquitous throughout the eastern United States. You’ll spot them in a wide variety of wooded habitats, from backyards to forests to swamps.
Gray Treefrog Range Map
They stick to the treetops until it’s time to breed. Gray Treefrogs prefer to mate and lay eggs in woodland ponds without fish. They’ll also use swamps and garden water features.
Gray Treefrogs are easier to hear than to see.
Listen for a high trill that lasts about 1 second, which is commonly heard in spring and summer.
*Gray Treefrogs are essentially identical to Cope’s Gray Treefrogs. The only way to tell the difference is to listen to their breeding calls. You can learn more by visiting this site.*
#6. Pickerel Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body length ranges from 2 to 4 inches.
- Dark green-brown coloration with two rows of dark squarish spots running down its back. Bright yellow color on the underside of hind legs.
- Females are typically darker and larger than males.
Pickerel Frogs prefer cool, clear waters in the United States. You can find them in ponds, rivers, lakes, slow-moving streams, and even ditches.
Pickerel Frog Range Map
During the breeding season, the males attract females with a low, snore-like call. The females will attach egg masses to branches in cool water, where the tadpoles will spend 87-95 days before becoming frogs.
Pickerel Frogs are the ONLY poisonous frog native to the United States.
When attacked, they produce toxic skin irritations that can be fatal to other animals and may cause skin irritation in humans if handled. As you can imagine, most predators leave them alone!
#7. Wood Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 1.5 to 3.25 inches.
- Coloration is various shades of brown, gray, red, or green, with females tending to be more brightly colored.
- Distinct black marking across the eyes, which resembles a mask.
As the name suggests, Wood Frogs are found in the United States in moist woodland habitats, including forested swamps, ravines, and bogs. They travel widely and visit seasonal pools to breed.
Wood Frog Range Map
This incredible little frog has a wide range across North America. They have adapted to cold climates by being able to freeze over the winter. Their breathing and heartbeat stop, and their bodies produce a type of antifreeze that prevents their cells from bursting. In the spring, they thaw and begin feeding again.
Interestingly, Wood Frogs seem to be able to recognize their family. Scientists have found that as tadpoles, siblings will seek each other out and group together!
Wood Frogs are one of the first amphibians to emerge after the snow melts.
Listen for a call that sounds a bit like a clucking chicken near vernal pools and other small bodies of water!
#8. Western Chorus Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body length up to 1.6 inches long.
- Smooth skin with color that varies from gray to green or brown.
- Dark brown or gray stripes that run down the back, dark stripe from the snout through the eye, and white stripe on the upper lip.
- Also called the Midland Chorus Frog.
In the United States, look for the Western Chorus Frog in woodland ponds, marshes, swamps, meadows, and grassy pools.
Western Chorus Frog Range Map
Credit: U.S. Geological Survey, Department of the Interior/USGS
For breeding, they try to find bodies of water without fish, including flooded fields, beaver ponds, roadside ditches, marshes, and shallow lakes and ponds. The female attaches small masses of eggs to underwater vegetation.
Western Chorus Frogs are secretive and nocturnal, so they can be hard to spot. Your best way to locate one is to use your ears.
Listen for a unique call that is rapid and relatively short and sounds a bit like running your finger over the teeth of a comb.
#9. Southern Leopard Frog
- Lithobates sphenocephalus
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 2 to 3.5 inches.
- Coloration is brownish to green with large darker green or brown spots on its back, sides, and legs.
- Lighter ridges extend down the sides of the back, and the upper jaw sometimes has a light, yellow stripe.
The Southern Leopard Frog will occupy various freshwater habitats in the United States. They are more terrestrial than many other true frogs and are often seen far from water. It’s also common to spot these frogs out on rainy nights!
Southern Leopard Frog Range Map
They breed during the winter and spring, particularly during periods of heavy rainfall. These frogs often nest communally, and the females attach egg masses to aquatic vegetation.
Make sure to listen for their low, chuckling croak! Some people describe the sound like a “squeaky balloon” or a “ratchet-like trill.”
For food, Southern Leopard Frogs primarily eat invertebrates, such as insects and crayfish.
#10. Northern Cricket Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults from 0.75 to 1.5 inches long.
- Irregular color patterns including grays, greens, browns, yellows, and blacks.
- A dark triangular spot between the eyes, blunt snout, warts, and dark banding on the legs.
This frog is one of the smallest vertebrates found in the United States!
But even though they are tiny, they can jump over 3 FEET in a single jump to escape predators, in addition to being excellent swimmers.
Northern Cricket Frog Range Map

Although Northern Cricket Frogs are part of the treefrog family, they don’t spend much time in trees. Typically you can find them in ponds and lakes with plentiful vegetation as well as slow-moving rivers.
This frog gets its name from its unique call. As you can probably guess, the Northern Cricket Frog makes a breeding call that sounds like the repeating chirp of a cricket.
#11. Southern Cricket Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are small and range from 0.5 to 1.25 inches long.
- Irregular color patterns, including black, brown, red, green, and gray.
- Dark triangle between their eyes and a bright-colored stripe running from their snout down their back.
This tiny frog is a great jumper, reaching heights of more than 60 times its body length!
Southern Cricket Frog Range Map
In the United States, the Southern Cricket Frog is primarily found in coastal plain bogs, bottomland swamps, ponds, and wet ditches. This species is extremely similar in both appearance and behavior to the Northern Cricket Frog.
As the name suggests, Southern Cricket Frogs give a distinctive, repetitive cricket-like chirping call.
#12. American Green Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults can grow up to 2.5 inches long and have smooth skin.
- Yellowish-green to lime green with pale yellow or white undersides.
- White stripes down their sides sometimes have black borders.
Even though they are common in their range, Green Treefrogs can be hard to find in the United States since they spend most of their lives high in trees. They also can change color based on light and temperature.
American Green Treefrog Range Map
During mating season, they visit ponds, lakes, marshes, and streams to breed and lay eggs. They prefer bodies of water with a lot of vegetation.
Their breeding call is a repeated, abrupt, nasal “bark.“ Sound is typically the best way to locate these treefrogs.
Green Treefrogs are often kept as pets. They are popular because of their attractive appearance, size, and how easy it is to take care of them. For example, they don’t require artificial heating like most amphibians. But being nocturnal, it’s unlikely you will see them moving around much, so they are probably not the most exciting pets!
#13. Pine Woods Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 1 to 1.5 inches long.
- Mottled coloring including browns, grays, reddish-brown, and grayish-green with dark markings on the back.
- Yellow, orange, or white dots can be seen on the back of the thigh when the leg is extended.
You’ll find the Pine Woods Treefrog in the United States in pine flatwoods, pine-oak forests, and cypress swamps. Spending most of their time high in the trees, these frogs have large sticky toe pads and minimally webbed feet.
Pine Woods Treefrog Range Map
During the breeding season, you can spot them in or near fish-free bodies of water, including shallow ponds, marshes, wetlands, cypress swamps, and ditches. The female lays eggs in shallow water where the tadpoles will live for about two months as they change into frogs.
These frogs give a unique sporadic or staccato chattering mating call which has earned it the nickname “the Morse code frog.”
#14. Barking Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 2 to 2.8 inches long.
- Most often bright green, but may also be gray, brown, or yellowish with dark spots on its back.
- Uniformly rough skin with light stripes down its sides.
The Barking Treefrog is the largest treefrog in the United States!
Barking Treefrog Range Map
You can spot Barking Treefrogs in various woodland habitats where they spend most of their time in trees and bushes. During the breeding season, they visit fishless wetlands where the female will lay her eggs. They also sometimes burrow into mud or rotten logs where they’re protected from predators.
These frogs are named for their explosive, loud “tonk” call, repeated every 1-2 seconds.
#15. Squirrel Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are around 1.5 inches long.
- Typically green, although individuals may be varying shades of yellow or brown with white or brown blotching.
- The upper lip is often yellowish, and they sometimes feature whitish stripes.
These small frogs are found in the southern United States in a variety of urbanized and natural habits.
Squirrel Treefrog Range Map
They can be seen on trees and buildings, in backyards, pine-oak forests, hardwood forests, floodplains, and pine flat woods. You might even find them visiting your porch to catch bugs that are attracted to the lights!
To breed, they visit wetlands like ephemeral pools, roadside ditches, and other small water bodies that lack predatory fish.
During the breeding season, you may hear their raspy, duck-like call.
#16. Little Grass Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are tiny and are around 0.75 inches long or less.
- Coloration is typically a pale brown or gray with a yellow or whitish underside, but individuals may have a green or pink tinge.
- A dark stripe extends from the nostril through the eye and down the side.
The Little Grass Frog is the smallest frog in the United States!
Little Grass Frog Range Map
These frogs can climb trees and bushes, but they are most frequently seen in marshy areas on grasses and sedges. During the breeding season, they visit shallow, often semi-permanent grass-filled water sources such as wetlands, roadside ditches, and seasonal ponds.
Listen for the males’ mating call, which is a high-pitched chirp or “tinkling” sound that is repeated every couple of seconds.
#17. Bronze Frog
- Lithobates clamitans clamitans
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 2 to 4 inches long.
- Bronze or brownish coloration with a white underside featuring dark, irregular patches.
- Raised ridges extend the length of the body, and they have large eardrums and webbed hind feet.
The Bronze Frog is actually a subspecies of the Green Frog.
They’re most commonly seen near permanent water bodies, including lakes, ponds, shallow streams, and swamps. They prefer areas with a lot of vegetation. Occasionally, you can spot Bronze Frogs in woodlands if it’s near their other preferred habitats.
Bronze Frog Range Map
Much like Green Frogs, the call of the Bronze Frog is thought to sound like a banjo string being plucked. They also have similar breeding habitats and lay eggs in shallow water, attaching the egg masses to vegetation.
#18. Crawfish Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 2.2 to 3 inches.
- Yellow to tan or brown with dark brown or golden circles over their body.
- White undersides.
Look for Crawfish Frogs in the United States in grassland and prairie habitats, including meadows and pastures.
Crawfish Frog Range Map
They get their name from their habit of living in crayfish burrows for most of the year. These frogs rarely stray far from the burrow as they offer protection from predators and weather, including winter frost and prairie fires.
During the spring, the frogs breed during mild, rainy weather. The males seek out seasonal pools and wetlands free from fish, such as flooded pastures, roadside ditches, and ponds.
Males attract females with a low, loud, snore-like call.
The Crawfish Frog is now listed as “near threatened” on the ICUN Red List. Their main threats include habitat loss, disease (chytridiomycosis), and competition with other frogs.
#19. Plains Leopard Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 2 to 3.75 inches long.
- Tan or light brown coloration with dark brown or greenish spots.
- A distinct white line on the upper jaw and lighter ridges running down the sides of the back.
As the name suggests, this frog is found on the plains of the United States.
Plains Leopard Frog Range Map
The Plains Leopard Frog is almost always seen around permanent bodies of water, including streams, creeks, ponds, and marshy areas. They primarily eat insects, although these opportunists will eat almost any living thing they can fit in their mouth (including other frogs).
During the breeding season, the males produce a guttural, rapid “chuck-chuck-chuck” call.
The Plains Leopard Frog is relatively common but can be hard to see. First, they are nocturnal. Second, they are shy and dive into the water as soon as they are approached!
#20. Pig Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 3.35 to 6.5 inches long.
- Green or gray-green coloration with brown or black blotching and a light-colored underside that may have dark spots.
- Fully webbed feet and a sharp-pointed nose.
Pig Frogs are a nocturnal aquatic species living in permanent bodies of open water like ponds and marshes. They rarely come to land, except for rainy nights.
Pig Frog Range Map
Pig Frogs get their name from their distinct mating calls. Listen for a low, grunting noise thought to sound like a pig, which can be heard in spring and summer.
These frogs are large! Some people in the United States even refer to them as Southern Bullfrogs because of their size. And like American Bullfrogs, they will eat anything they can fit in their mouth, although their primary food is crayfish.
#21. River Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 3 to 5 inches long.
- Rough, wrinkled skin that is dark to blackish green with a dark gray.
- Distinctive white spots on lips, particularly the lower lip, which distinguishes them from bullfrogs.
Contrary to its name, the River Frog can be found in the United States in various aquatic habitats, including lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes, and streams. Unlike many aquatic frog species, the River Frog is easy to approach!
River Frog Range Map
The females lay eggs in large floating masses amongst aquatic vegetation. Once hatched, tadpoles may take up to two years to mature into adult frogs.
To attract a mate, males produce a deep, low, roaring snore-like call.
#22. Mink Frog
- Lithobates septentrionalis
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 1.9 to 3 inches.
- Coloration is green with darker green or brown blotches. Cream, yellow, or white underside.
- Bright green lips and webbed hind feet.
The Mink Frog gets its name from the unusual scent it produces when handled. It’s believed to smell like a mink or rotting onions!
Mink Frog Range Map
These small frogs are primarily aquatic and can be found in ponds, lakes, swamps, and streams, particularly in wooded areas. They favor areas with water lilies which they utilize for protection from predators.
During the breeding season, the males produce a rapid series of croaks thought to sound like tapping a hammer on wood.
When large numbers of Mink Frogs gather together in the United States and croak in chorus, many people think it sounds like horses walking down a cobblestone street. 🙂
Interestingly, tadpoles remain in the larval stage for a year before turning into a frog!
#23. Boreal Chorus Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 1 to 1.5 inches long.
- Coloration is brown, olive green, or tan with three dark stripes down the back that are sometimes broken into blotches.
- Prominent black stripe on each side from nostril, through the eye, and down the sides to the groin.
- Looks very similar to the Western Chorus Frog. Boreal Chorus Frogs are distinguished by having shorter legs.
While the Boreal Chorus Frog can be common in the United States, they are rarely seen. They’re small and secretive, inhabiting moist meadows and forests near wetlands.
Boreal Chorus Frog Range Map
Credit: U.S. Geological Survey, Department of the Interior/USGS
These frogs breed in shallow temporary ponds and pools such as flooded fields and roadside ditches. They require waters free of fish; otherwise, most of their eggs and tadpoles would be eaten!
Males produce a loud chorus of calls at breeding sites, which are easy to identify.
The sound has been compared to someone running a finger over the teeth of a comb (“reeeek“). You’re most likely to hear the calls in the late afternoon or evening.
#24. Blanchard’s Cricket Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 0.6 to 1.5 inches long.
- Warty skin is typically tan, brown, olive green, or gray with darker banding on the legs.
- Dark triangular mark between the eyes on the head.
Blanchard’s Cricket Frogs can be found in or near permanent bodies of water in the United States, including bogs, lakes, ponds, marshes, and slow-moving rivers and streams. They can also sometimes be spotted in temporary bodies of water such as flooded fields and drainage ditches as long as there is a permanent water source nearby.
Blanchard’s Cricket Frog Range Map

Interestingly, although they are in the “treefrog” family, they spend most of their time on the ground and in the water.
Unfortunately, Blanchard’s Cricket Frogs are declining in parts of their range and are considered threatened. They face habitat loss, chemical contamination, and competition for resources. Another pressure they face is their short life span, as the average individual only lives one year.
Males make unique, repetitive, metallic breeding calls.
The calls are thought to sound like two pebbles or marbles being clicked together. The females lay small clusters or even single eggs, and the tadpoles emerge in late summer.
#25. Pacific Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults can reach 2 inches long, with the males typically being smaller.
- Most are green or brown with pale white undersides, but some are reddish, gray, cream, or black.
- Dark mask across the eyes to the shoulders and uniformly bumpy skin.
The Pacific Treefrog can be found in a wide range of elevations in the United States, ranging from sea level to 10,000 feet (3,050 m)!
Pacific Treefrog Range Map
Look for them in woodlands and meadows. Interestingly, these frogs spend most of their time on the ground despite being a treefrog. They even hide from predators in underground burrows!
The Pacific Treefrog travels to the shallow water of ponds and lakes to breed and lay eggs. The female attaches the eggs to sticks or other underwater debris.
Also called the Pacific Chorus Frog, this species can be heard during the spring.
Their mating call is a two-part call that sounds like “kreck-ek” or “rib-bit.“
#26. Coastal Tailed Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are 0.9 to 2.1 inches long.
- Rough skin with a coloration of brown to olive green. Large, flattened head with a light triangular mark between the snout and eyes.
- Slightly webbed hind feet, hard toe tips, and the males have a tail-like extension of their cloaca.
This species might be the most unique frog in the United States!
Coastal Tailed Frog Range Map
Unlike most other species, the Coastal Tailed Frog is found in steep, fast-moving, rocky streams. This habitat has caused this species to develop several unique adaptations.
They have reduced lung size, likely to control buoyancy, and hard toe tips to help them travel along the bottom of these streams. They also have a greater number of vertebrae than other frogs. Lastly, these frogs lack ear membranes, which means they CAN’T vocalize.
Tailed frogs get their name from a unique habitat adaptation, the male frog’s cloacal extension. This extension is used to insert sperm into the female so it isn’t lost in the fast-moving water. They are the only North American species of frog to reproduce through internal fertilization.
The females lay strings of eggs under rocks in the stream. The tadpoles have a large oral sucker which allows them to attach themselves to smooth stones in turbulent water. It takes the tadpoles one to four years to mature into adult frogs.
#27. Cascades Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 1.5 to 3 inches long.
- Typically green or brown with dark gray or black spots on their back.
- Small bumps on their back and sides, a dark mask, and a white jawline stripe extending to the shoulders.
This frog is named for where it was first discovered, which is the Cascade Mountains! They’re typically found in ponds, lakes, marshes, or slow-moving streams between 2,182 and 8,038 ft (665 and 2,450 m) in elevation.
Cascades Frog Range Map
The males make a breeding call during the day and night from above and underwater. Listen for a sound that is a series of low, chattering, grating, and clucking noises.
You may spot their bicolored eggs, which are black on top and white on the bottom, floating in masses near the shore. Tadpoles mature in 3-4 months, depending on the water temperature.
Interestingly, the skin of Cascades Frogs secretes an antimicrobial substance that helps protect them from pests and infections. Talk about self-healing!
#28. Canyon Treefrog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults range from 1-2 inches in length.
- Typically brown, gray-brown, tan, or gray-green with darker, irregular blotches on the back. They often match the color of their habitat.
- They sometimes appear golden in direct sunlight, and the inside of the hind legs is bright yellow.
Canyon Treefrogs are found in rocky areas in the southwestern United States. They may be called treefrogs, but this species is mainly found perched on boulders and rock faces near permanent water sources.
Canyon Treefrog Range Map
During the hottest part of the day and periods of low rainfall, Canyon Frogs will seek shelter in rock crevices. They sometimes cluster together in these areas to help reduce moisture loss. They also have tougher skin on their back than most frog species to help them cope with their hot, dry climate.
You may hear the male’s low call during the breeding season, which is sometimes thought to sound like a distant sheep or goat. Since they are nocturnal, your best bet is to hear one at night.
Breeding occurs during spring rains, and the females lay large masses of 100 or more eggs which float in the water.
#29. Rio Grande Leopard Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 2.2 to 4.5 inches.
- Coloration is tan, brown, or pale green. Dark brown or black spots, pale ridges down their back, and cream-colored undersides.
- Angular, pointed noses, and long powerful legs.
Rio Grande Leopard Frogs live in grasslands, savannas, shrublands, and deserts but are never found far from water. Since they are primarily nocturnal, your best time to see them is at night when they are hunting for insects.
Rio Grande Leopard Frog Range Map

Unlike many other species, these frogs don’t hibernate and are active year-round in the United States. When it does become too cold, they will burrow underground for protection.
These frogs mate during rainy periods of spring and fall. The male makes a distinctive rattling call which can be heard from one mile away! Interestingly, competing males will sometimes make a chuckling call to try and confuse females.
The females lay large masses of eggs, which they attach to aquatic vegetation. After hatching, the tadpoles slowly mature into adult frogs over the course of about three months. Adult frogs reach sexual maturity and begin breeding at around three years of age.
#30. Northern Red-legged Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 2 to 5.25 inches, with the females being larger.
- Reddish-brown to gray with dark specks and blotches, dark mask, and light stripe on the jaw.
- Yellow underside with red on the lower abdomen and hind legs.
The Northern Red-legged Frog is typically found in the United States near slow-moving streams and ponds. They prefer shaded areas with plenty of emergent vegetation, which they use as defense from predators.
Northern Red-legged Frog Range Map

These frogs require cool water temperatures to reproduce, so the breeding season begins early, between January and March. The males select territories and produce a soft mating call with 5-7 repeating notes sounding a bit like, “uh-uh-uh-uh-uh.” They make this call both under and above water.
The females produce large egg masses, which they attach to rotting logs and submerged vegetation typically 5 to 6 inches below the water surface. Believe it or not, Northern Red-legged Frogs can live for 12 to 15 years!
#31. Foothill Yellow-legged Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adult body lengths range from 1.5 to 3.2 inches.
- Coloration is gray, brown, or olive green, sometimes with darker mottling and a buff triangular patch on the snout.
- Granular skin and yellow underside of hind legs and lower abdomen.
The Foothill Yellow-legged Frog can be found up to 6700 feet above sea level on the western slopes of the Cascade and Sierra mountain ranges. Look for them in the United States in rocky streams and rivers with open, sunny banks.
Foothill Yellow-legged Frog Range Map
Sadly, this frog has disappeared from much of its range. It faces threats from habitat loss from dams and polluted waters from agricultural pesticides.
Unlike many frogs, the male’s breeding call is rarely heard. They produce a series of 4-6 low-pitched, raspy notes and predominately call underwater and at night. The females attach egg masses to the downstream side of submerged rocks and pebbles in slow-moving streams. The tadpoles become adult frogs in roughly 3 to 4 months.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lVKB9MyQ6Lg
Interestingly, Foothill Yellow-legged Frogs secrete a unique substance through their skin which is key to helping prevent fungal infections!
#32. Sierran Tree Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults can reach 2 inches long, with males typically being smaller.
- Dark mask across the eyes to the shoulders and uniformly bumpy skin.
Sierran Tree Frogs are mainly found in the western United States in forests.
Adults typically appear as shades of either brown or green. But interestingly, individuals can change colors over the course of a few hours to help them blend into their environment. So if you find one and come back to find it later, it may look completely different. 🙂
The Sierran Tree Frog has an interesting, if not confusing, history. These frogs used to be known as Pacific Tree Frog (Pseudacris regilla), but in 2006, a scientific paper came out that split Pseudacris regilla into three species:
- Pacific Tree Frog (Pseudacris regilla), Baja California Tree Frog (Pseudacris hypochondriac), and the Sierran Tree Frog.
Unfortunately, the paper did not provide any way to tell the difference between these three species, nor any maps as to where each one is primarily found. While this change has been controversial, it has stuck over the years.
#33. Eastern Narrow-mouthed Toad
- Gastrophryne carolinensis
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults only grow up to 53 mm (2.1 in).
- Pointed snout with an oval-shaped body.
- They vary in color from grey and brown to green. A dark brown stripe is usually seen on both sides of the body.
Don’t let the name fool you! Despite being called a “toad” and looking and acting like one, Eastern Narrow-mouthed Toads are frogs, scientifically speaking. They belong to the family Microhylidae.
These “frogs” are hard to find in the southeastern United States because they are fossorial, which means they spend most of their life underground. They are found in a wide range of habitats as long as it provides their two favorite things; moisture and shade!
As far as food is concerned, Eastern Narrow-mouthed Toads rely on ants! Believe it or not, ants make up 95% of their diet.
Since they spend so much time underground, the best way to find one is to use your ears! They have a loud, piercing call that resembles a high-pitched sheep. Listen below.
#34. Columbia Spotted Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Green or brown with black spots on its back
- The upper lip and belly are white.
- Compared to other frogs, they have shorter back legs, upturned eyes, and a narrower snout.
You will almost always find Columbia Spotted Frogs near permanent bodies of water, such as ponds, lakes, slow-moving streams, and marshes. In addition, they need lots of vegetation to provide adequate protection because many different predators hunt them!
Females lay up to 1,300 eggs at a time in shallow water. Interestingly, once laid, this mass of eggs absorbs water and can grow to the size of a softball! And these eggs are not attached to anything, so they just float around until the tadpoles are ready to hatch.
To attract a female, male frogs will sing a song that ranges from long, deep sounds to clicks. You can listen to an example of the clicks below:
#35. Upland Chorus Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- They are different shades of brown with darker blotching on the body.
- Small frogs that grow between 0.75–1.5 inches (1.9–3.8 cm) in length.
- Look for a white line above the upper lip.
Due to their nocturnal and secretive nature, Upland Chorus Frogs are RARELY seen in the eastern United States.
The best chance you have to find one is at night, immediately after it rains.
In addition, you won’t find Upland Chorus Frogs in water, as they are terrestrial. They live in a variety of different habitats as long as it’s relatively moist, provides ample vegetation for hiding places, and is near a permanent source of water.
Unlike most other frog species, it is also fairly hard to HEAR one. But if you are lucky and are in the right place at the right time, it would sound like this:
#36. Cajun Chorus Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Most adults are light brown with three brown stripes that run along the back.
- Small frogs that grow up to 1.2 inches (30 mm) in length.
The Cajun Chorus Frog has only recently been described as its own distinct species. Previously, it was considered to be an Upland Chorus Frog (Pseudacris feriarum). But analysis of mitochondrial DNA, mating calls, and appearance showed that Pseudacris fouquettei is, in fact, a separate species.
Like other chorus frogs, they are hard to find! They are nocturnal and are typically only seen after a heavy rainstorm at night.
These amphibians can be found in various habitats in the southern USA, such as forests, grasslands, and marshes, as long as there is adequate moisture and vegetation to hide amongst.
Listen to the mating calls of the Cajun Chorus Frog below!
#37. Spotted Chorus Frog
Identifying Characteristics:
- Typically olive-green with darker green botching on their back.
- Adults grow to a maximum of 1.25 inches (3–4 cm).
Spotted Chorus Frogs, also known as Clark’s Tree Frogs, are typically only seen at night in since they are nocturnal. But even if you venture out after dark to find one, you will probably still have some difficulty because they are so small. In the United States, they only live in Texas, Oklahoma, and southern Kansas.
Despite being considered tree frogs, these amphibians are found in habitats without many trees, such as prairies, grasslands, pastures, meadows, shrubby areas, the edges of forests, and even on lawns if it’s near a breeding pool.
Although they are primarily terrestrial, they require a source of water nearby to thrive. During droughts, they head underground and become inactive.
#38. Greenhouse Frog
- Eleutherodactylus planirostris
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are tiny and measure only 17 to 31 mm (0.67 to 1.22 in) in length.
- Olive-brown coloration.
- Some adults have two darker stripes running down their backs, while others have dark blotching.
This frog species is NOT native to the United States.
Greenhouse Frogs are from Cuba and other islands in the West Indies. But they have made their way to the southeast United States and now are relatively common living around people.
But these frogs are hard to find! They are small, nocturnal, and mostly live in moist leaf litter. The best time to find one is on a warm, rainy night during summer.
The eggs and tadpole stages of Greenhouse Frogs are unique. First, instead of laying a giant mass of eggs like other frogs, they lay them singly in damp locations, buried under debris or logs. Second, the tadpole stage happens entirely while in the egg! So fully developed juvenile frogs hatch directly from the eggs and are only about 5 mm long.
Listen to their mating call below!
#39. Rio Grande Chirping Frog
- Eleutherodactylus cystignathoides
Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults are tiny and only measure between 16–24 mm (0.6–0.9 in).
- Dark brown with darker spots. Their back legs usually have dark crossbars.
Despite their small size, Rio Grande Chirping Frogs thrive around people in Texas and Louisiana. They are often found in urban areas in lawns and gardens at night, hiding under backyard objects during the day to escape the heat.
Their range has slowly expanded because of humans! These small frogs often hide on potted plants, which get sold and transported to new areas.
Rio Grande Chirping Frogs are unique because BOTH males and females produce calls! But, interestingly, it’s not known exactly why females call.
#40. California Treefrog

Identifying Characteristics:
- Adults grow up to 2 inches in length.
- Grey or light brown coloration resembles granite stones, which provides excellent camouflage.
- Dark brown blotches on warty, rough skin.
California Treefrogs are not really found in trees. Their preferred habitat is along streams, where they are found amongst boulders, quiet pools of water, and shade.
California Treefrog Range Map
They are mostly nocturnal. During the day, look for them under rocks and between rock cracks. If you find one, they are not very shy and can easily be handled.
At night, their calls can become deafening.
Listen for a loud, low-pitched quack that sounds a bit like a duck!
Do you need additional help identifying frogs in the United States?
Try this field guide!
Which of these frogs have you seen in the United States?
Leave a comment below!